Background
The company is a well-known internet enterprise specializing in an online spatial design software platform, empowering designers from renovation companies, home furnishing, whole-house customization, and commercial decoration sectors.
Challenges
In the post-pandemic era, market uncertainty has significantly increased, leading to a surge in challenges. To achieve its goals, the company quickly outlined its digital transformation plan, focusing on the pre-sales, mid-sales, and post-sales business chain.
In the post-sales sector, the implementation costs and labor costs for customer support have risen alongside business growth, resulting in substantial annual expenditures. The company has identified cost optimization in this sector as one of its core construction goals, aiming to reduce overall costs by at least 5% annually.
The company’s CIO, with 15 years of experience in the digital field, led multiple rounds of evaluations on the costs of various third-party SAAS and in-house development options at the project’s inception. After thorough analysis, it was concluded that adopting our solution and technological foundation could effectively reduce development costs and improve implementation efficiency, leading to a long-term partnership.
Value
The company conducted a rigorous digital outcome analysis of the project, verifying it from four perspectives: system usage, quality, human efficiency, and cost. The results are as follows:
- System Usage: All clients and business units are operational, with a DAU of 200+.
- Quality Perspective: Accurately filtered out pseudo customer demands, reducing the proportion of pseudo demands by over 20% within a year, directly saving training costs.
- Human Efficiency Perspective: Reduced single merchant training demand by 25% and shortened communication cycles by 35%.
- Cost Perspective: Achieved the initial project goal of optimizing overall costs by 5%.
Core Application Scenarios
Merchant Training: Full-chain Automation from Demand to Training
The company’s merchant training service involves assigning training tasks to internal or external trainers with different capability tags by the training supervisor.
Previously, when a client or business initiated a training request, the supervisor had to manually assign an appropriate trainer. Due to the lack of standardization in client training needs, trainer capability profiles, and trainer schedules, about 25% of the trainers’ efforts were spent on coordinating client training requests. It could take up to a week from the client’s request to the arrangement of training, resulting in low efficiency and client satisfaction.
After the system went live, client training requests were standardized and digitized, and trainer profiles and schedules were also digitized. Through algorithmic demand matching, the process from submitting a training request to a trainer accepting the task, as well as student and trainer check-ins and post-training feedback collection, was largely automated.
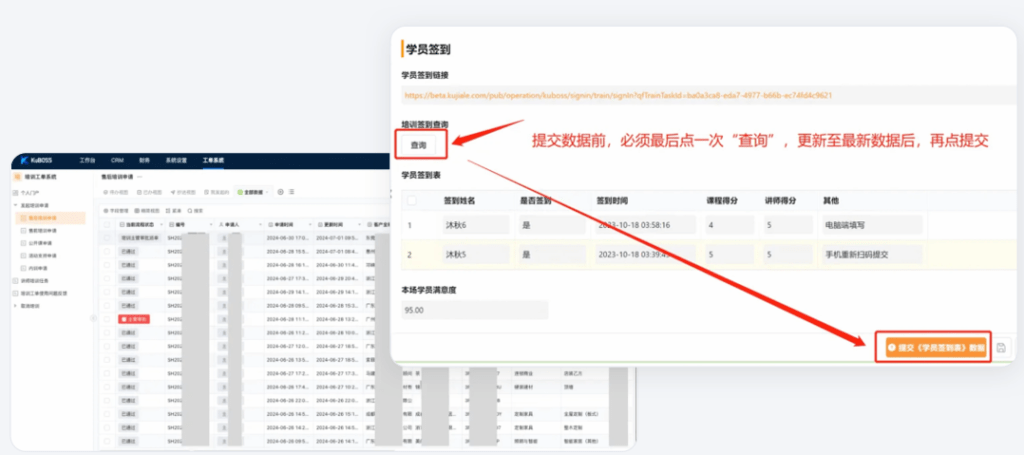
The dispatching algorithm considers not only the trainer’s profile and schedule but also geographical factors, dynamically matching the nearest available trainer based on their schedule location.

As a result, the communication efficiency from the client/business request, through resource scheduling, to training delivery and client satisfaction evaluation has significantly improved, with trainer efficiency alone increasing by nearly 25%.
Merchant Modeling
The software supports custom models for merchants, which is one of the company’s business models. However, the previous operational model had two main issues:
- Inefficient Reconciliation: The diverse charging models for optimizing client modeling needs, including platform subsidies and ecosystem service provider premiums, made cost allocation and settlement work highly complex. Model operation colleagues spent about a week each month on reconciliation, leading to inefficiency.
- Difficulty in Mining Client Needs: Previously, merchant modeling needs were mostly stimulated and collected through sales, making the demand heavily influenced by sales and lacking a channel for clients to provide active feedback.
In terms of reconciliation and settlement, once merchant modeling needs were digitized, the system could automatically calculate amounts by linking client industry, model demand quantity, and type, effectively improving operational efficiency by nearly 25%.

Model operation workstations can accept client demands, connect with the ecosystem, and integrate demands from clients, the platform, and third parties. With flexible permission settings, the model demand initiation process is directly open to clients, allowing service providers to be directly involved in the system for collaborative processing.
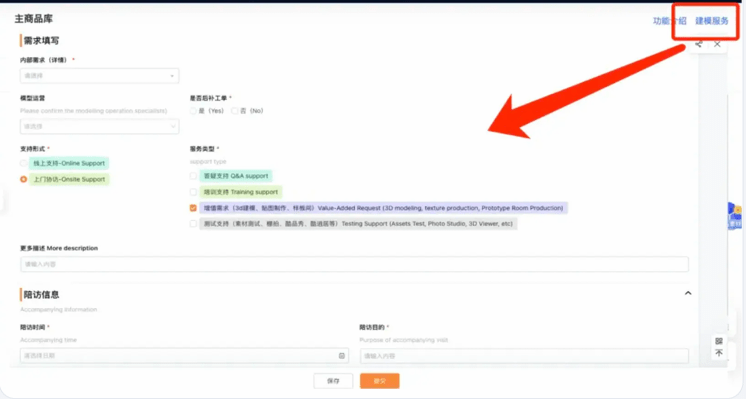
Clients can click the “Modeling Service” button on the interface to submit demands. Once approved, they can confirm the quotation and proceed directly to payment. Third-party service partners log in to the system via internal SSO to receive model development tasks as to-dos.
Merchant API: Building Intelligent Customer Service to Improve ROI
Through the merchant API application, the company aims to address the unmet client demands similar to modeling and improve the efficiency of API inquiries.
By adding and opening up demand submission channels, merchant clients with API service needs can propose demands more quickly and conveniently without going through the business side, similar to the modeling application.
Unlike the modeling aspect, API services involve a large number of client inquiries, resulting in relatively low ROI.
To this end, the system standardized and normalized customer service tickets, continuously providing new materials and bases for inquiries to improve efficiency.
After accumulating some knowledge, the system further offered an AI intelligent customer service robot solution to intercept basic inquiries, significantly enhancing customer service efficiency.